How to Make MS Word Documents Accessible
All guidelines for website content apply for Word documents. Please refer to the general Web Content Accessibility Guide first and then check that your document is compliant with the Microsoft (MS) Word accessibility requirements mentioned below.
A MS Word document cannot be made fully accessible on the browser. Use the desktop Word app to access all features required in this guide.
Table of Contents
Titles, Headings & Fonts
- Name your file in an accessible format that is easily understandable. Save your file.
- Good: Summer Events on Cochran Campus
- Bad: File12_Events_Ver.1
- Use the default text styles from the “Home” tab on the top menu.
- Use common sans-serif fonts such as Arial or Calibri. Avoid writing in all caps and using different fonts.
- Body paragraphs use the “Normal” styling
- To add emphasis, use the “Strong” styling to bold text or the “Emphasis” styling to italicize text. Assistive technology does not recognize bolded or italicized text in MS Word.
- To create a numbered or bulleted list, make sure to use the default list styling tools. Do not mimic the look of a list by adding custom symbols + space + text as assistive technology cannot recognize it as a list.
- Press Ctrl+F to open the Navigation panel. Click “Headings” and check that your headings are in the correct reading order.
Images
Add alt text by clicking on the image, clicking “Format Picture,” and typing in alt text in the Alt Text field.
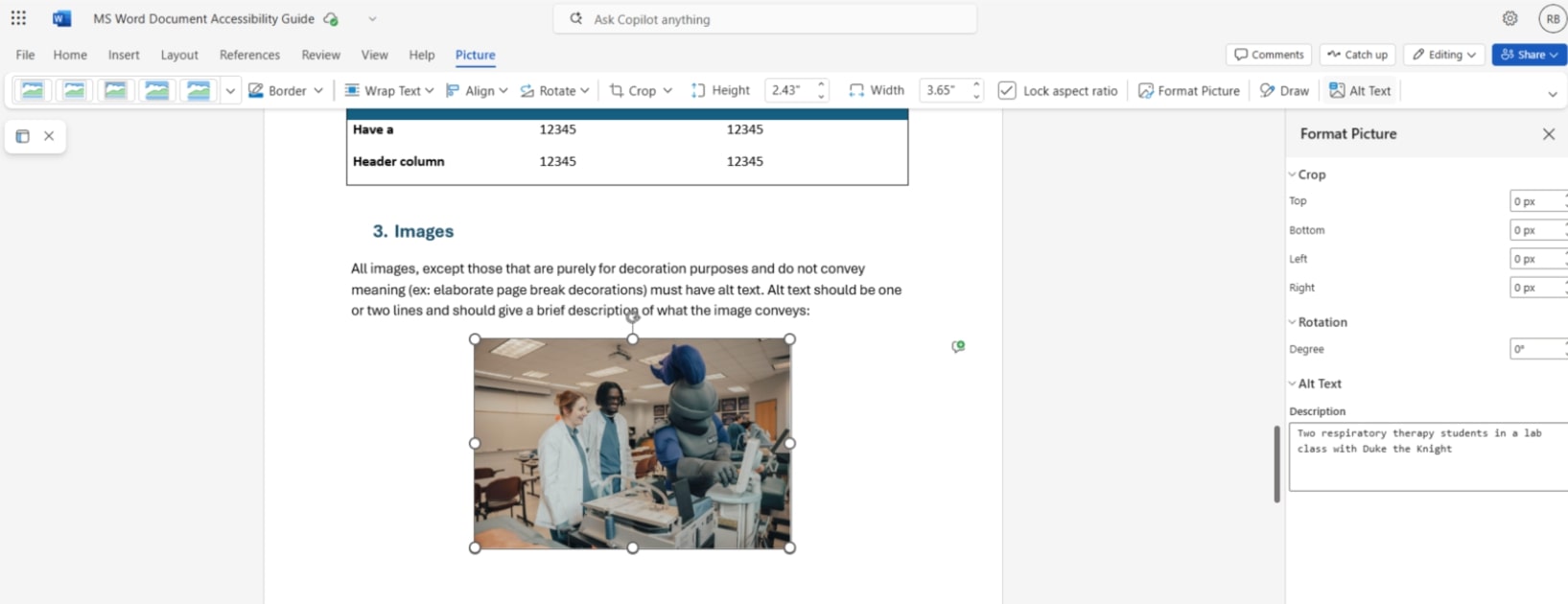
Exception: Alt text for repeated images used for layout and decorative purposes, such as annotations, page breaks, headers, and footers, should be left blank to signal assistive technology to ignore reading these elements on every page. However, any important content placed inside them must be included in the body of the document to be accessible.
Tables
WCAG requires that all “Information, structure, and relationships conveyed through presentation can be programmatically determined or are available in text” (see 1.3.1. Info and Relationships requirement).
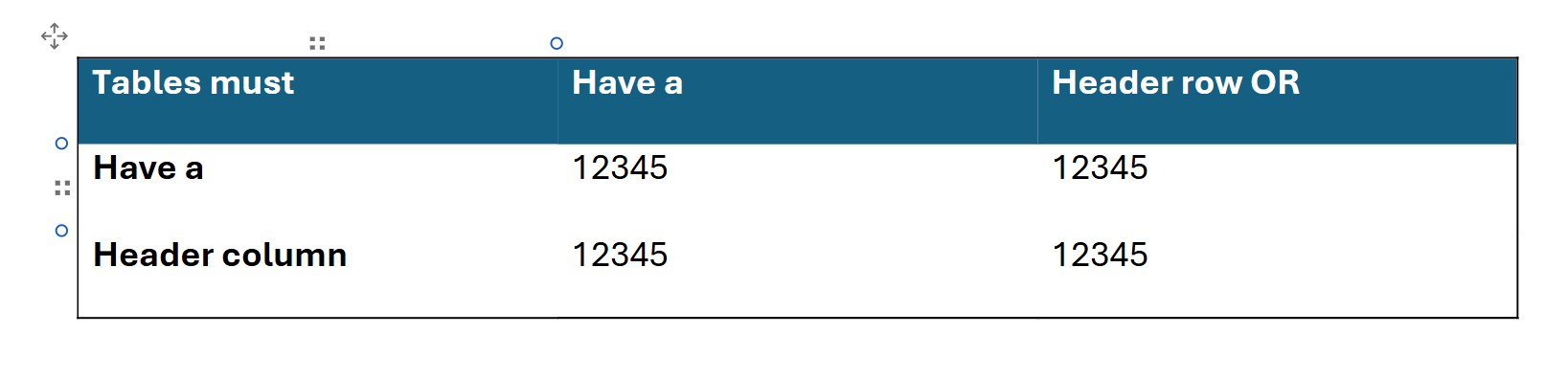
Tables require an extra step to make programmatically accessible. Avoid using tables if you can. If possible, present the content in another way (e.g., bullet list).
To make tables accessible, use the “Table” tab in the top menu and click on “Style Options” to choose “Header Row” and/or “First Column” for your table. Using these preset layouts ensures that accessibility tools recognize that the table has a clear, labeled format.
Go to “Layout” on the top menu and click on “Repeat Header Rows.”* This will ensure that screen readers recognize that there is a header row, especially if the table takes up more than one page.
*Repeat Header Rows is only available on the desktop Word app.
Creating a Table of Contents (TOC)
Note : Do NOT mimic the look of a TOC from text and spacing alone. It will not be accessible.
- Go to the “References” tab on the top menu.
- Click on “Insert Table of Contents.”
- Adjust the TOC from the right-click “Format Table of Contents” settings.
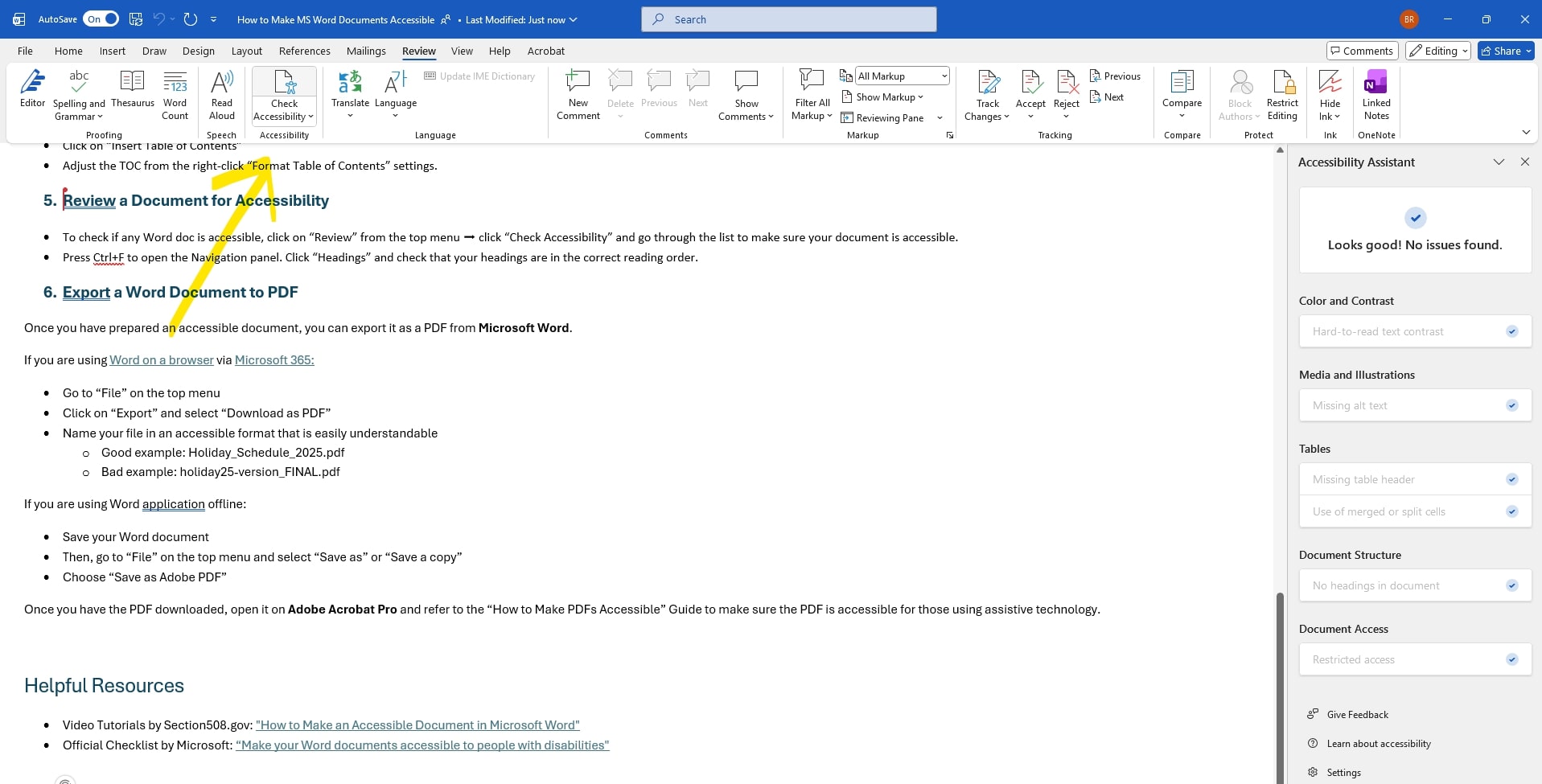
Review a Document for Accessibility
- To check if any Word doc is accessible, click on “Review” from the top menu ➡ click “Check Accessibility,” and go through the list to make sure your document is accessible.
- Review your document using the “Immersive Reader” feature. Go to “View” ➡ “Immersive Reader” ➡ “Read Aloud.”
Export a Word Document to PDF
Once you have prepared an accessible document, you can export it as a PDF from Microsoft Word.
If you are using Word on a browser:
- Go to “File” on the top menu
- Click on “Export” and select “Download as PDF”
If you are using the Word desktop app:
- Save your Word document
- Then, go to “File” on the top menu and select “Save as” or “Save a copy”
- Choose “Save as Adobe PDF”
Once you have the PDF downloaded, open it on Adobe Acrobat Pro and refer to the “ How to Make a PDF Accessible” Guide to make sure the PDF is accessible for those using assistive technology.
Helpful Resources
- Video Tutorials by Section508.gov: " How to Make an Accessible Document in Microsoft Word"
- Official Checklist by Microsoft: “ Make your Word documents accessible to people with disabilities"