Web Content Accessibility Guide
On May 28, 2025, the University System Office of Legal Affairs and Information Technology Services issued web accessibility guidance that "will require all state entities to make their web content and mobile applications accessible to individuals with disabilities by April 24, 2026."
To simplify the compliance guidelines, this guide covers accessibility requirements that all MGA content creators must adhere to. This guide will focus on how to use Cascade, the University's Content Management System (CMS), to create accessible content for all MGA websites.
- Watch the MGA accessibility webinar and Q&A recording and view the presentation slides.
- For guidance on how to use Cascade, please visit the Cascade User Resources page.
Table of Contents
Headings
Text headings must be used in sequential order and must not be skipped. Headings should be marked as headings from the source HTML code.
Do not adjust font type and size to mimic a header style. Assistive technology can only identify headers by using the source code, not their visual features (for more info, read the WCAG 1.3.1. Info and Relationships requirement).
In Cascade, you can select heading levels using the Formats tab in the page editor. Start from Heading 3. Headings 1 & 2 are reserved for the office/department name and page title (Title & Display Name fields) for each page. Refer to the Cascade Style Guide for more information.
Colors
Text and background must have a color contrast ratio of 4.5:1 to be read easily. Large text, such as heading levels 1 and 2, must have a contrast ratio of at least 3:1 (For more info, read the WCAG 1.4.3. Contrast (Minimum) requirement).
This standard applies to anything using colors, including designs, images, or charts/data visualization on the website. Exceptions include text within logos and inactive decorative elements that are not visible.
Using an accessible color palette generator can help you select the right colors to use. To remediate existing images, use a color contrast checker to make sure it passes accessibility standards.
Color Contrast Checkers
- WAVE browser extension
- Coolors.com contrast checker
- Venngage accessible color palette generator
- Coblis colorblindness simulator - test your image here before uploading it live
- TPGi Colour Contrast Analyser - this app opens in a separate window
For go-to MGA color combinations, refer to the MGA Brand Guidelines page.
Use
- White text on MGA purple background
- Black text on white background
- Black text on light gray background

Avoid
- Purple text on black background
- Black text on purple background
- Purple text on any dark color
- Color combinations that are not colorblindness-friendly:
- Red & green
- Green & brown
- Green & blue
- Blue & gray
- Blue & purple
- Green & gray
- Green & black

Images
Alt Text
All non-text content that is presented to the user has a text alternative that serves the equivalent purpose (For more info, read the WCAG 1.1.1 Text Alternatives requirement)
Alt text should provide a short, descriptive summary of the image that focuses on why that image is included. Many platforms have a feature that allows you to create alt text.
Image with Text
If the image contains text, such as a quote or an event flyer, you must include the words on the text, verbatim, in the alt text field.
Image with Too Much Text
If you cannot include all text on the image/graphic in the alt text field, provide a summary of the content and a link where visitors can click to read more details.
For images with too many details, try splitting up the text: only include key information in the image and move the rest of the text to a caption or a separate web page (image description example link).
Exception: Decorative Images
Decorative images do not need alt text. Decorative images are annotations (e.g., elaborate page breaks), symbols, or images that do not convey meaning, add no useful information to the content already provided, and are placed just for layout purposes.
- For example, the School of Computing's Coffeehouse Series flyers are marked as decorative because all relevant information on the flyer image is included in the page as plain text.
- For more details on how to write good alt text and how to tell which images are decorative, please visit the Section508.gov guide on alt text.
How to Add Alt Text in Cascade
- For images on mga.edu website page: right-click on the image from the page editor → click “Image,” → type in the “Image Description” field.
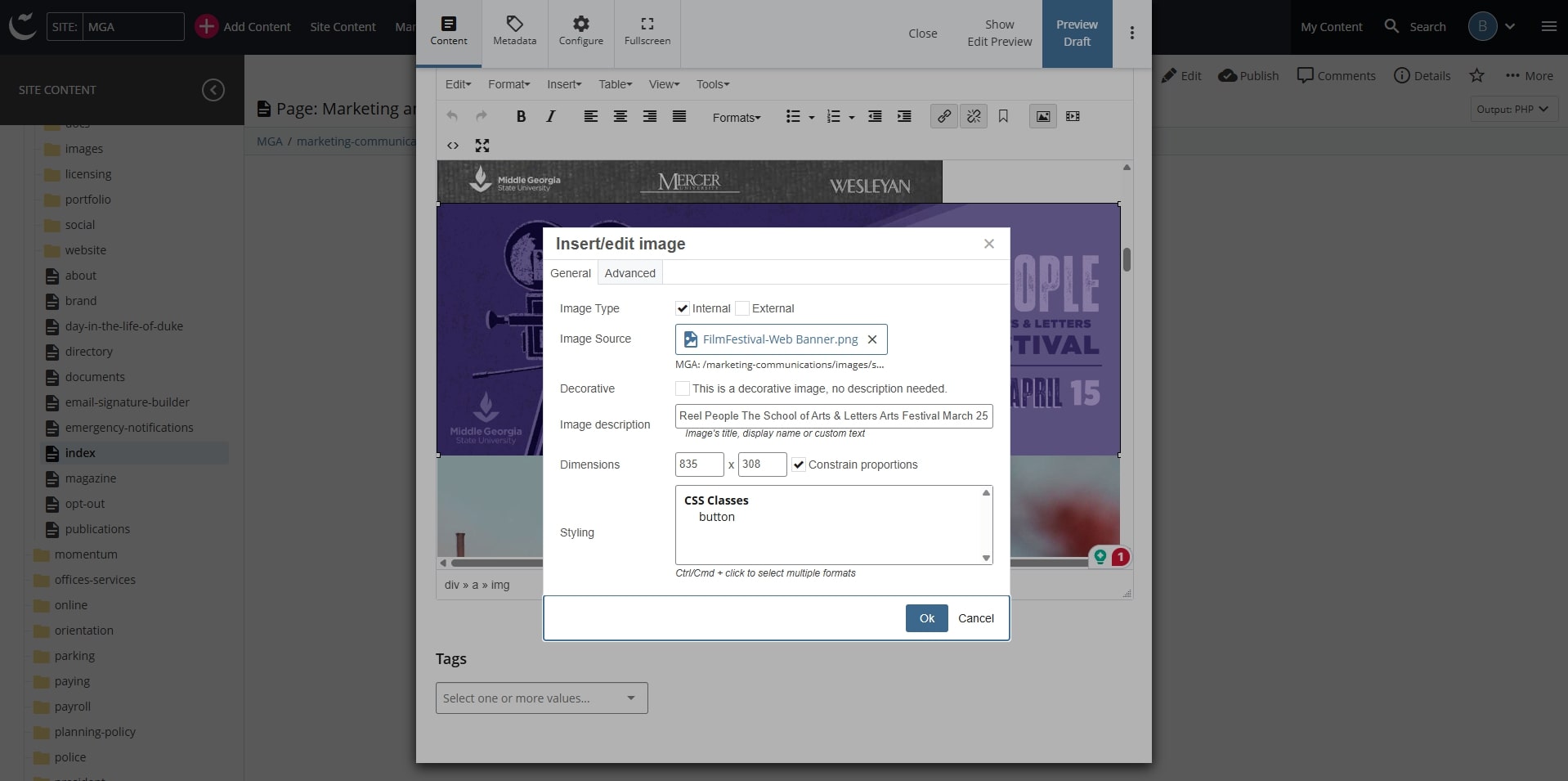
- For blog sites: scroll down and type in the "Image Alt Text" field.
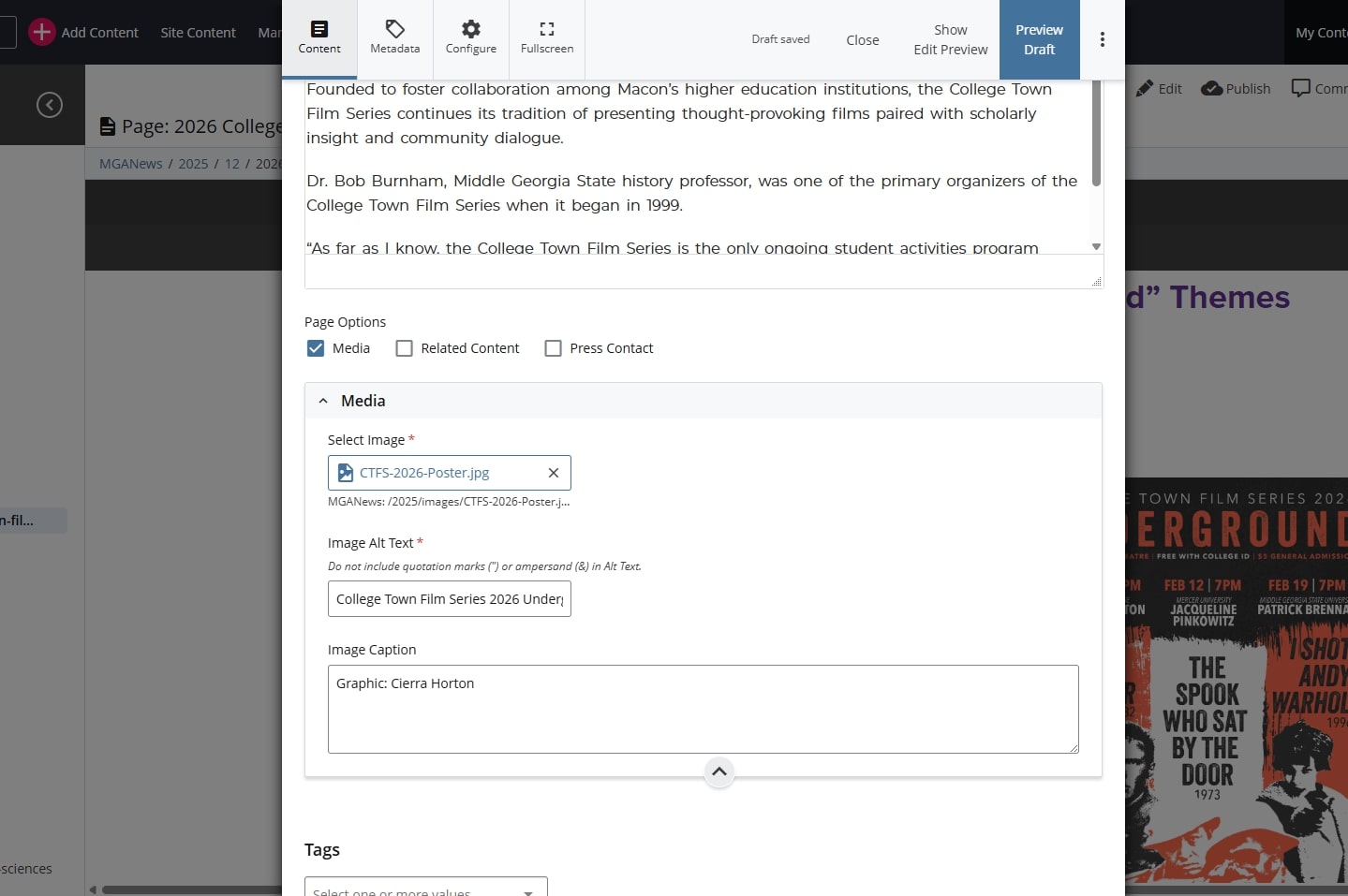
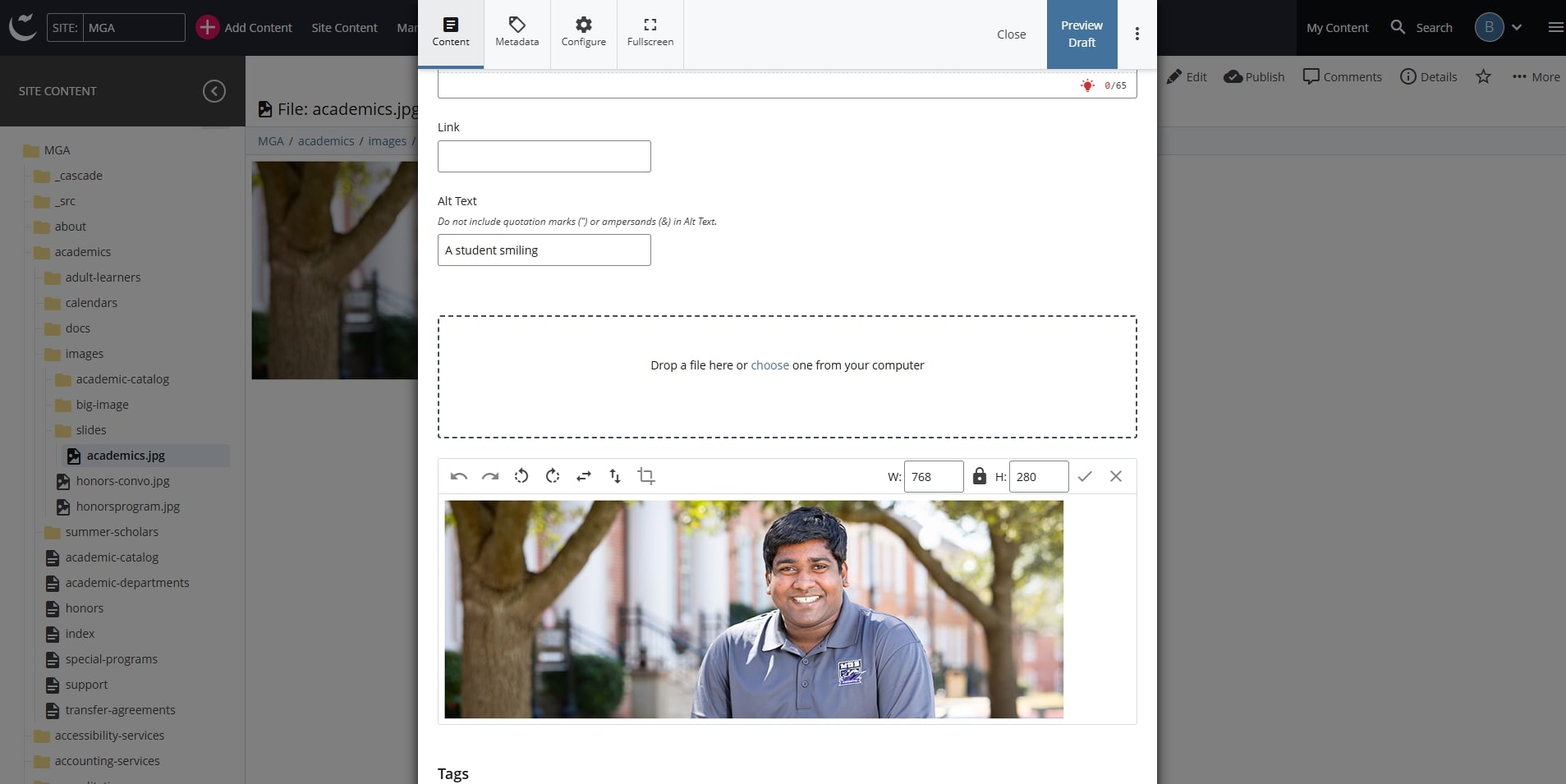
- For slideshow images: alt text must be added from the file editor within the department/office’s “slides” folder. Type in the “Alt Text” field. This field only applies to slideshow images and must not be used to write alt text for any other type of image.
Tools for Creating Images
Adobe InDesign
Adobe InDesign is the go-to platform available to all MGA faculty and staff for creating accessible images, flyers, designs, and more. If you do not already have access to the Adobe Creative Cloud, reach out to the MGA Helpdesk to request access.
*For creating accessible PDFs, refer to the “How to make a PDF Accessible” Guide.
Canva
Canva is great for creating print material but for uploading images for website use, it is unfortunately not an accessible authoring tool. This means designs created with Canva that are posted on the website require alternate versions (e.g., a flyer and an HTML web page with the same info) to be considered accessible.
Image Checklist by Category
Refer to the following checklist for the image category that applies to your image before uploading to Cascade.
Images for Website Page Content (mga.edu)
- Image file size is under 200KB
- Image dimensions are around 200px x 200 px (minimum) to 600 x 600px (maximum), dimension ratio can vary
- Image file format is JPG
- Image file name is readable (ex: cochran_summer_painting_event_2025.jpg)
- Image is uploaded to the “images” folder for that is most relevant to the page you are working on (ex: /about/campuses/images)
- Image has alt text
- If the image contains text, the content must be duplicated in the body text and the image must be marked as decorative (leave alt text blank)
Blog Site Images
- Image file size is under 200KB; Do NOT use original images downloaded as is (file size is too big)
- Image dimension does not exceed 360px width
- Image file format is JPG
- Image file name is readable (ex: cochran_summer_painting_event_2025.jpg)
- Image is uploaded to the “images” folder for that year (ex: 2025/images)
- Image has alt text.
- If the image contains text, the content must be duplicated in the body text and the image must be marked as decorative (leave alt text blank)
Header Images (big-image)
- Image file size is under 200KB
- Image dimensions are 1920 x 462 px (minimum) to 1920 x 1000px (maximum)
- Image file format is JPG
- Image file name is readable (ex: cochran_summer_painting_event_2025.jpg)
- Image is marked as decorative (alt text must be blank)
Slideshow Images (slider)
- Image file size is under 200KB
- Image dimensions are 960 x 350px
- Image file format is JPG
- Images have alt text in the “Alt Text” file editor fields.
- The "slides” folder does not exceed 5 images
How to Reduce File Size & Convert from PNG to JPG
There are multiple ways to reduce an image’s file size, and many image editing tools allow you to download it as a JPG. Choose a method that works best for you:
- Save a screenshot
Take a screenshot of your image, save it, and convert file from PNG to JPG using a free tool (ex: https://png2jpg.com or Adobe Express) - “Save for Web" in Adobe Photoshop
Open the image in Photoshop. Go to File > Export > “Save for Web.” Adjust the size, quality options, and set preset to JPEG. Make sure the edited version follows the image sizing guidelines. Click “Save.” - Use Canva
Use the “custom size” feature to easily upload images and save them in a consistent size. I recommend downloading the image as a PNG and converting it to JPG to avoid losing image quality.
Videos
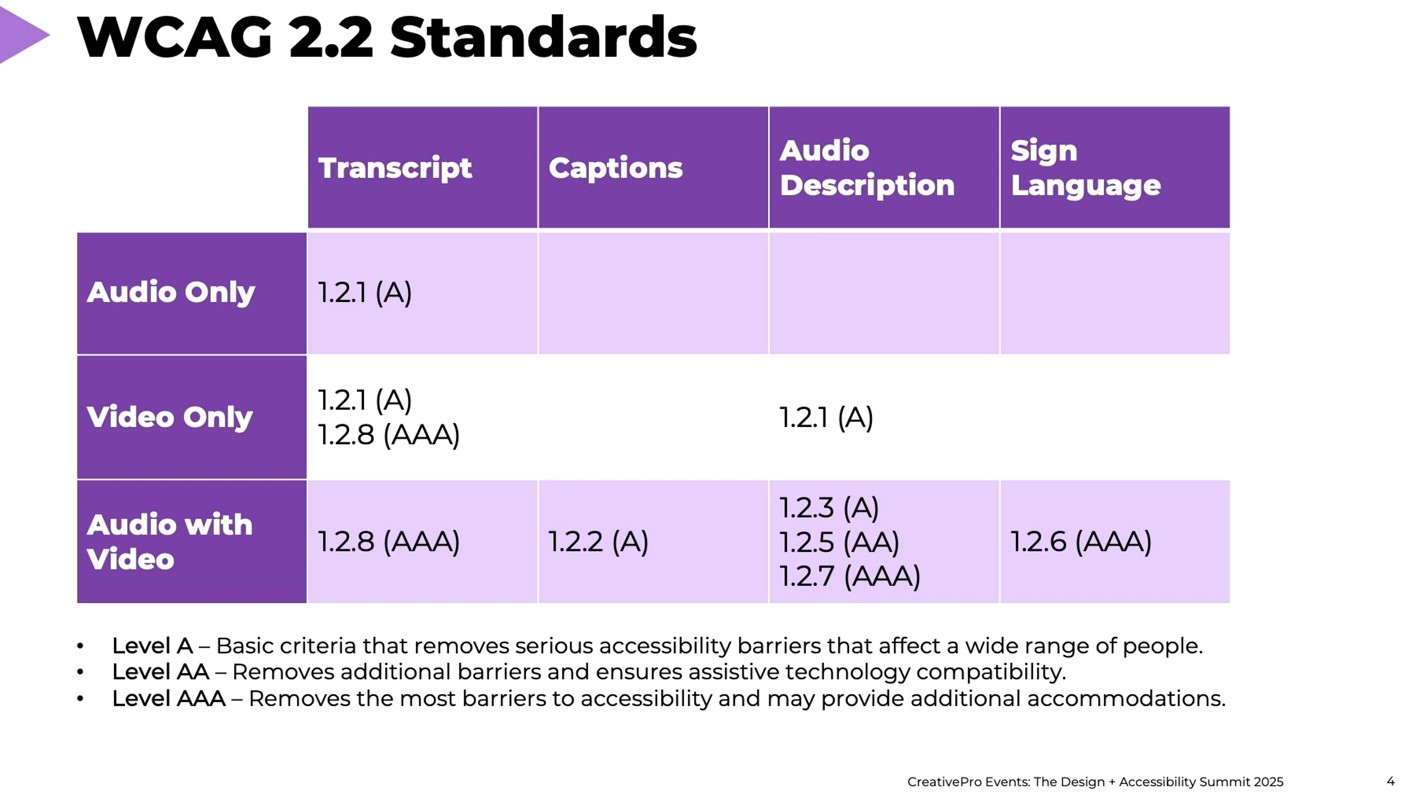
To meet ADA Title II compliance requirements, video content created within MGA and by third-party contractors must provide the following:
- Transcripts for audio-only content (e.g., podcasts, music, etc.)
- Transcripts for video-only content (ex: decorative videos for website, existing GIFs)
- Captions for video with audio (ex: State of the University recordings)
- Audio descriptions or transcripts for video-only content (ex: header video for home page)
- Audio descriptions for audio with video; only if important visual content is not mentioned or explained in audio (ex: presentations, virtual tours, etc.)
Transcript vs. Caption vs. Audio Description
- Transcripts are a separate file that has a written recording of the audio [ examples]
- Captions are included in the video and can be open-caption (included in the video) or closed-caption (can be turned on/off) [example]
- Refer to Transcribing Audio to Text, a guide by W3C
For video transcripts and captions, it is recommended to begin with the original document for the video, such as a script, or use the auto-generation tools provided on YouTube and make edits as needed.
Charts & Data Visualizations
Although charts and graphs are necessary to present information in an easily organized way, they must also be made accessible.
- The same rules for using color, images, and alt text applies to charts & data visualizations.
- Alt text for a chart should highlight one key takeaway. Avoid describing the chart and focus on conveying impact.
- Good example: 2025 had the highest enrollment of students.
- Bad example: The blue bar shows 2025 data. The yellow bar shows 2024 data.
- Data should not be labeled by color alone (e.g., “Refer to the red line for 2025 trends”). Add labels, legends, and patterns in your charts & tables to convey meaning in more ways than one. For more info, read the WCAG 1.3.3 Sensory Characteristics requirement.
- Refer to the Data Visualizations, Charts, and Graphs, a guide by Harvard Accessibility Services
Links
When adding links to your content, avoid using “click here,” “learn more,” “go here,” and other standalone phrases. It is recommended that you use the full title or name of the page you are linking to. For more info, read the WCAG 2.4.4 Link Purpose (In Context) requirement.
- Good example: Visit the Residence Halls page to view images of each on-campus residence, floor plans, and details.
- Bad example: View more images, floorplans, and details about each residence hall. Click here.
When sharing links to the MGA website to the public, never use the beta.mga.edu preview links. Beta preview links are intended for internal faculty & staff review for page content and design before a page goes live on the website. Check to make sure you are using the live website link before sharing it to the public via hyperlink, printed material, etc.
PDFs & Word Documents
If at any point the content you create gets exported in the following formats, please follow this general web content guide and refer to these additional format-specific guides to make sure the final format of your content is ADA Title II-compliant: